gvSIG-Desktop 1.12. Manual de usuario
- Legend types
Legend types
Introduction
In this tab you can define, in an advanced manner, the type of legend with which you want to represent the data of layer, from its fields [1].
[1]: It must be noted that you can not use the fields resulting from a join to make legend classifications, meaning that, to use these fields in a legend you will have to export the shp resulting from the join.
You can choose the following forms of representation:
Quantities
Four types of legends can be found:
Point density
Defines a legend of a point density based on the value of a certain field.
Labelling field A drop-down menu opens where you can choose fields from the table (Double or Integer types) from which you can make a legend which represents the quantity of each value in the table. The properties of the points which represent the density of the values in the table can be changed.
- Point size: Use the arrow to change size of the point.
Point value: This is the numeric value which will be given to each point that is drawn.
- Colour: Choose the colour of the point by clicking on the button located right of the colour.
- Background colour: Choose the background colour.
- Outline: Click on this button if you want to give an outline to the symbol.
Intervals
This type of legend represents the elements of a layer using a range of colours. The gaps or graduated colours are mainly used to represent numeric data which have progression or range of values, such as population, temperature, etc.
Classification field: A drop-down menu where you can chose the attributes of the layer for which you want to make the classification for. The field must be numerical as it is a gradual classification (by the rank of the value)
- Interval type: There are three types of intervals from which to choose. These are:
- Same intervals: Calculate same intervals from values which can be found in the chosen field to make the selection.
- Natural intervals: The number of intervals are specified and the sample of this number is divided into this number according to the Jenk method of optimisation of the natural localisation of intervals.
Cuantil intervals: The number of intervals are specified and the sample is divided into this number but gathering into groups values according to their order. Number of intervals: Should indicate the rank or interval number which defines their classification.
- Nº of intervals: Type in the nº of intervals to be represented.
- Initial and final Colour: Select the colours that will be used to graduate. The initial colour for lower values and the final colour for the higher ones.
- Calculating intervals: Once the above options have been defined, click on the “Calculate intervals” button to show the final result. The default symbols and labels that appear can be modified by clicking on them, just as in the previous cases.
- Add: New ranks to the calculations can be added.
- Remove all / Remove: Allows you to delete all (remove all) or some (remove) of the elements which make-up the legend.
Graduated symbols
Represents quantities through the size of a symbol showing relative values.
- Classification field: Choose the numeric field for which the classification is to be made.
- Interval types: The same that are in legend type Intervals
- Symbol: Modify the symbol size with a minimum value (From), to a maximum value (Until). You can also modify all the features of a specific symbol by clicking on the “Template” button, as well as its “background”.
- Calculating intervals: Once the above options have been defined, click on the “Calculate intervals” button to show the final result. The default symbols and labels that appear can be modified by clicking on them, just as in the previous cases.
- Add: New ranks to the calculations can be added.
- Remove all / Remove: Allows you to delete all (remove all) or some (remove) of the elements which make-up the legend.
Proportional symbols
Represents quantities through the size of the symbol which shows exact values.
- Classification field: Choose the numeric field for which the classification is to be made.
Normalisation fields: Possibility of choosing a numerical field which normalises the results, maintaining the proportion of quantities.
- Symbol: Modify the symbol size with a minimum value (From), to a maximum value (Until). You can also modify all the features of a specific symbol by clicking on the “Template” button, as well as its “background”.
Categories
Expressions
Shows layer elements according to a certain filtered expression.
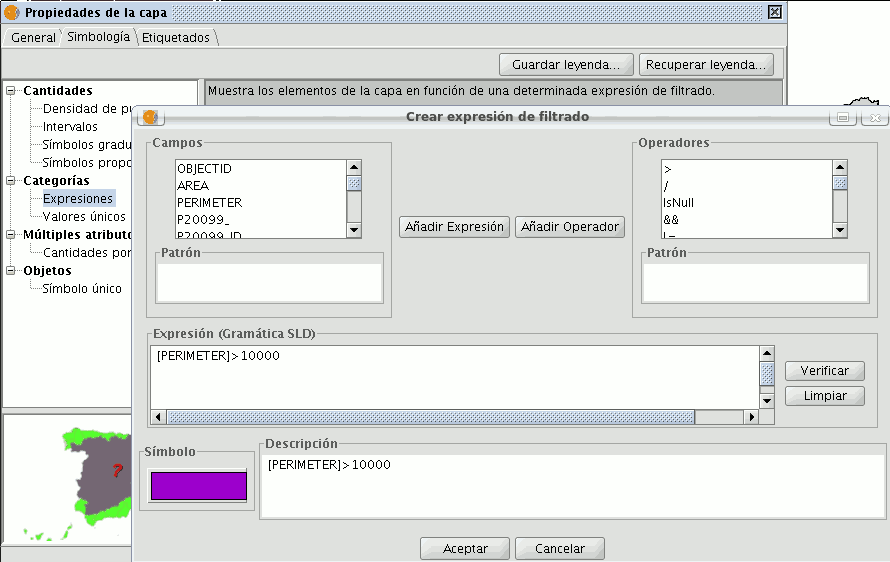
- ''New filtered expression:'' A new window opens where you can configure expressions (filters) upon which a certain symbol will be applied. Each of these will be shown as a row in the main window of this type of legend. The syntax these filters use is SLD.
- ''Modification of filtered expression:''You are able to modify an expression by selecting it.
- ''Delete a filtered expression:''You are able to delete an expression by selecting it.
- ''Up/Down buttons:'' Allows you to move the created expressions up or down so that they later have that order in ToC.
Unique values
Each register can be represented with an exclusive symbol according to the value it adopts in a certain field in the attributes table. It is the most efficient method for spreading categorical data, such as municipalities, floor types, etc.
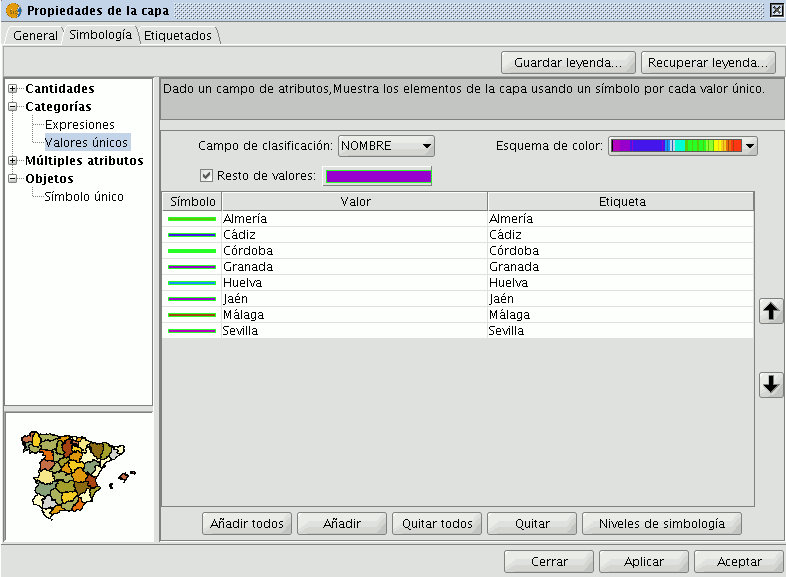
You will find the following symbology configuration options:
- ''Classification field:''A drop-down menu opens where you can select the layer which contains the data to carry out the classification, in the attributes table field.
- ''Add all/Add:'' Once the “classification field” is selected, all the different values are shown by assigning a symbol (colour) different to each by clicking on the “Add All” button. These symbols can be modified by clicking on them. By default the label (name that appears on the legend) is similar to the value that is adopted by this field. By clicking on “Add” you can add new values to the list.
- ''Delete all/Delete:'' Allows you to delete all (delete all) or some (delete) of the elements that make up the legend.
- ''Symbol properties:'' If you right click on any of the “cells” on the “Symbols” you can modify its properties specifically through the “Select symbol” and “Symbology level” buttons, as well as being able to change the label name in TOC.
Multiple attributes
Category quantities
Represents quantities for each category.
For this, it combines two fields (which must be of a numeric type), applying a combined legend made up of colour ramp (for field_1) and specific gradual symbols (for field_2).
Meaning that this type of legend combines a a representation of intervals based on the values of Field_1 with anothier representation of gradual symbols based on the values of field_2.
Chart or diagram legends are intended to provide a visual representation of data in a table, thereby communicating a lot of information very easily.
In particular this extension allows two types of legends to be constructed:
- The first one is represented by circular diagrams known as Pie Charts. The pie chart shows the proportional size of the elements of a data series, based on the sum of its parts, and with each sector representing the value of a particular field. It always shows only one data series and is useful when you want to emphasize a significant element.
- The second type of legend is represented by diagrams known as Bar Charts or Bar Graphs. A bar graph, also known as a column graph, is a diagram containing rectangular bars with lengths proportional to the values they represent. Bar graphs are used to compare two or more values.
The pie legend is located in the Multiple attributes section of the legend tree, and can be used to represent several attributes at once. To access it, right-click on the layer name to open the Properties and then select the symbols tab.
The following options are available for configuring the pie charts:
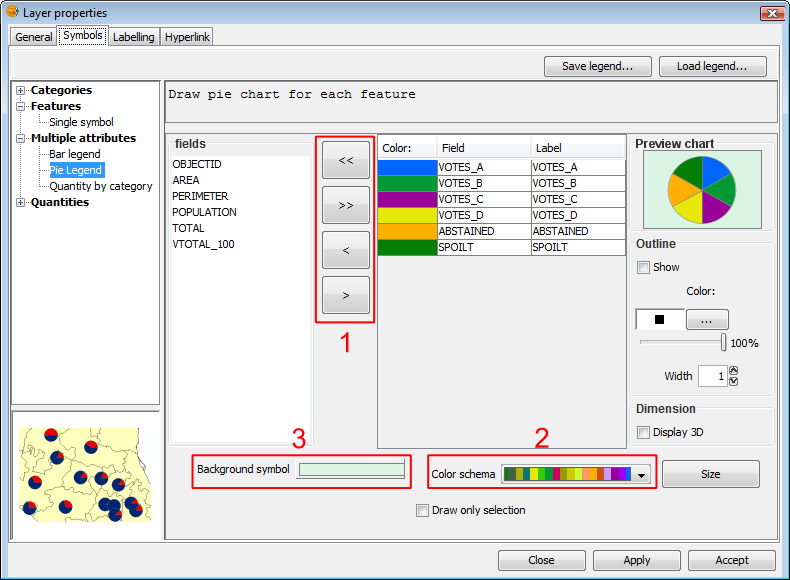
Symbols. Pie legend
Fields: You can choose which of the layer's fields to represent, provided they are numeric. With these fields you can:
- Add all fields.
- Delete all fields.
- Add the selected fields.
- Delete the selected fields.
To do this click on the buttons shown in the image above (Box 1).
Colour scheme: You can change the default colour scheme for the pies. To do this select the desired "Colour scheme" from the drop-down list, as shown in the image above (Box 2).
Change the colour: In addition it is possible to change the colour of pie slices once they have been added.
Once the default colour scheme has been chosen, the colour of a pie slice can be changed by double-clicking on its color.
The following dialog is displayed where you can select a colour sample or set it yourself (HSB, RGB).
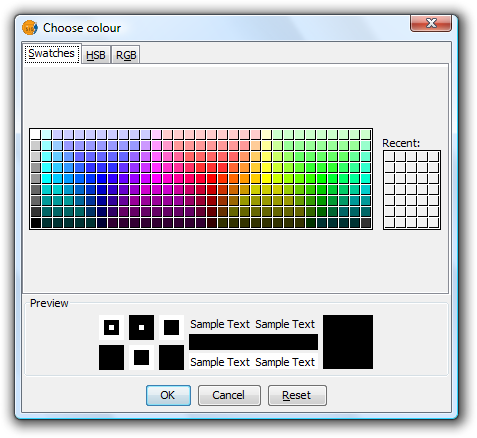
Symbols. Color Selection
Background symbol: You can change the symbol of the background geometries by clicking on the symbol to open the symbol editor (pictured above, Box 3).
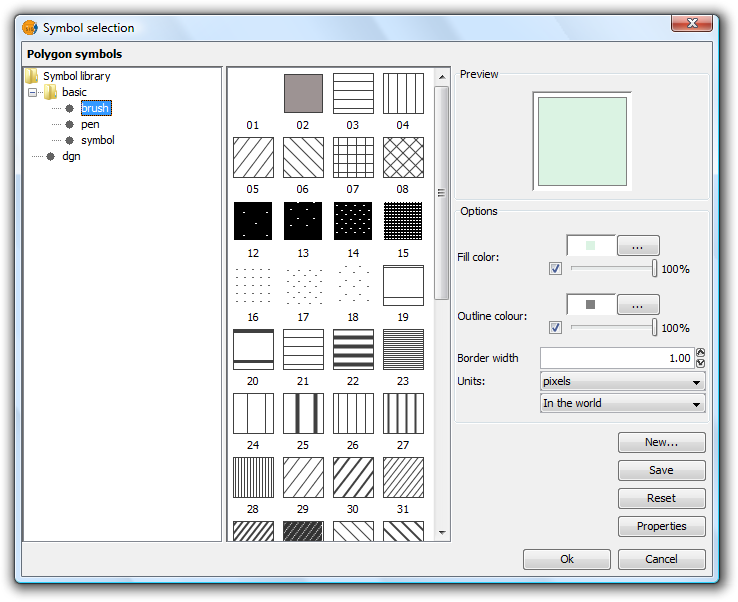
Symbols. Symbol Selector
Outline: You can display an outline with a specified colour and thickness around the pie slices. Tick the "Show" check box to draw outlines around the pie sectors.
Dimension: Tick the check box to display the pie in 3D. By default the pie is drawn in 2D.
Preview chart: Any changes made are reflected on the chart preview.
Click the 'Size' button located in the pie legend configuration screen.
Pie Legend. Size button
Clicking this will open the following dialog:
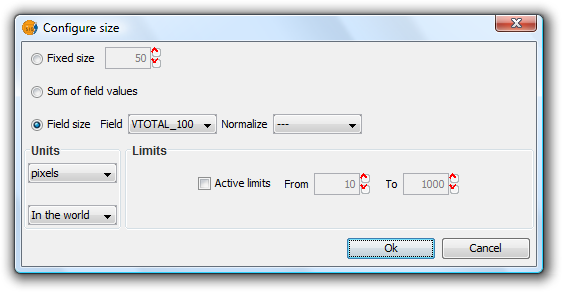
Pie Legend. Configuring size
There are three options for setting the size of the diagrams:
- Fixed Size: All the pie charts will have the size indicated here.
- Sum of field values: The size of the pie charts is obtained from the sum of all the records of the fields making up the chart.
- Field size: The size is obtained from the selected field and can be normalized if so desired.
In addition to setting the size of the pie, the units can also be specified.
Units: Select units (meters, pixels ...) and representation (in the world or print layout), depending on your requirements. If the units are set to "in the world" then the size will depend on the View's zoom level, while selecting "print layout" results in a fixed size, both on the screen and when printed.
Active Limits: Limits can be specified if the size of the chosen field size is not set to the "Fixed Size" option.
Activating limits for the other options sets the minimum and maximum values of a particular measure (Sum of field values or Field size). Taking the limits into account, the intermediate field values are calculated in proportion to the values of the records of the field, or to the sum of the field values.
This option is used to restrict the drawing of pie charts to selected geometries.
The geometries can be selected either before or after configuring the pie chart size and display options.
In order to represent pie charts for selected geometries, simply activate the check box Draw only selection in the pie legend configuration dialog.

Check to display pie charts for selected geometries only
The following image shows an example in which pie charts are only shown for selected geometries (shown in yellow).
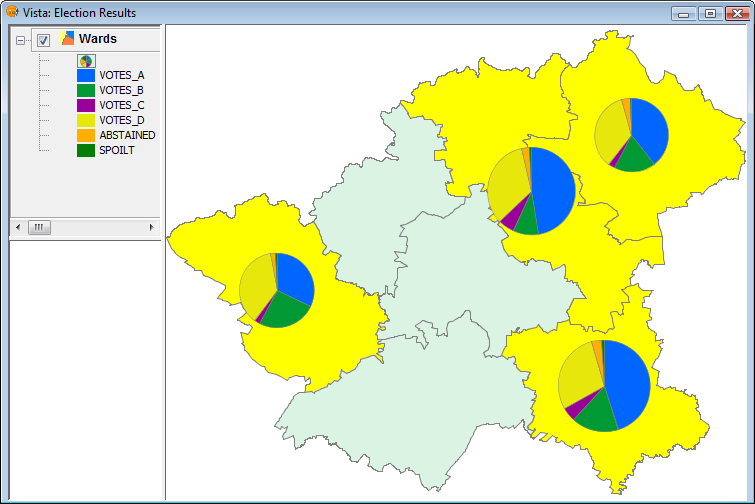
Example showing pie charts for selected geometries
The bar legend is located the Multiple Attributes section of the legend tree, and can be used to represent several attributes at once. To access it, right-click on the layer name to open the Properties, then select the Symbols tab.
The following options are available for configuring bar charts:
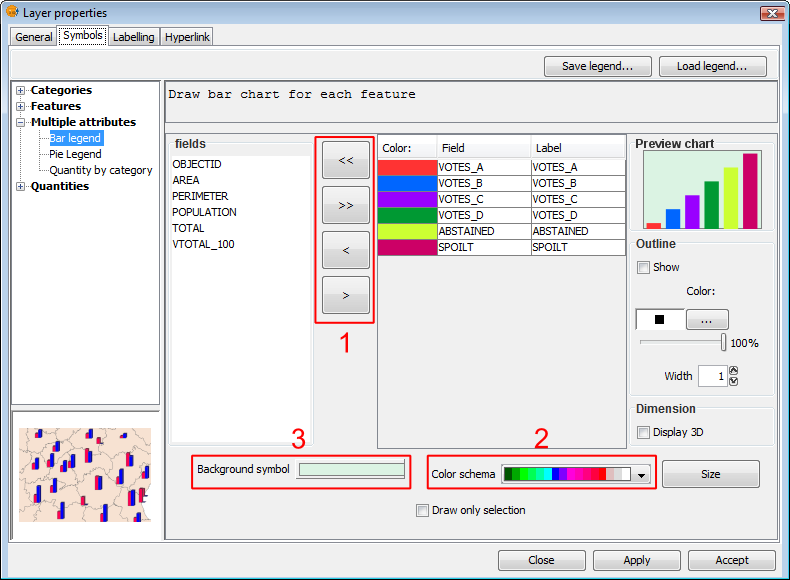
Symbols. Legend bar
Fields: You can choose which of the layer's fields to represent, provided they are numeric. With these fields you can:
- Add all fields.
- Delete all fields.
- Add the selected fields.
- Delete the selected fields.
To do this click on the buttons shown in the image above (Box 1).
Colour scheme: You can change the default colour scheme for the bars. To do this, select the desired "Colour scheme" from the drop-down list, as shown in the image above (Box 2).
Change the colour: In addition it is possible to change the colour of bars once they have been added.
Once the default colour scheme has been chosen, the colour of a bar can be changed by double-clicking on its color tile.
You can use the following dialog to select a colour sample, or set it yourself (HSB, RGB).
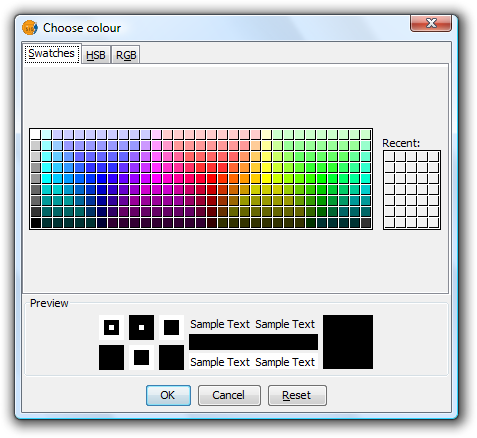
Symbols. Color Selection
Background symbol: You can change the symbol of the background geometries by clicking on the symbol to open the symbol editor (pictured above, Box 3).
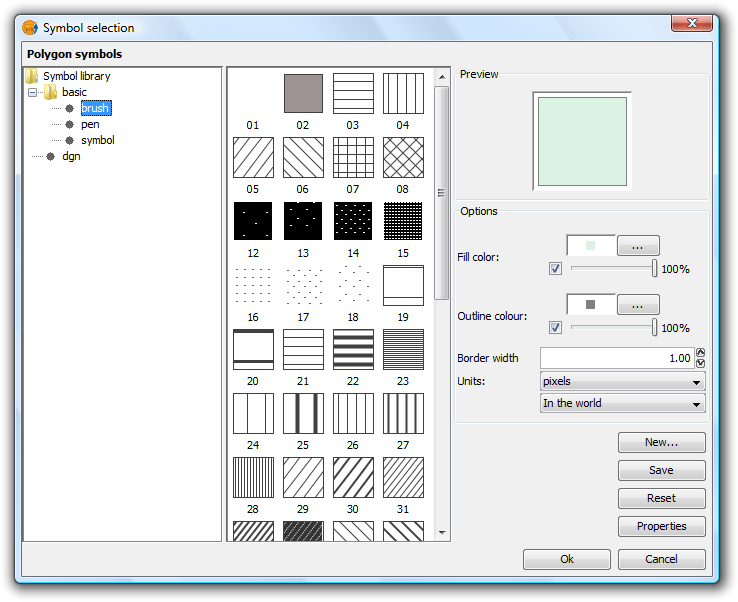
Symbols. Symbol Selector
Outline: You can display an outline with a specified colour and thickness around the bars. Tick the "Show" check box to draw outlines around the bars.
Dimension: Tick the check box to display the bars in 3D. By default the bars are drawn in 2D.
Preview chart: Any changes made are reflected on the chart preview.
Click the 'Size' button located in the bar legend configuration screen.
Bar Legend. Size button
Clicking this will open the following dialog:
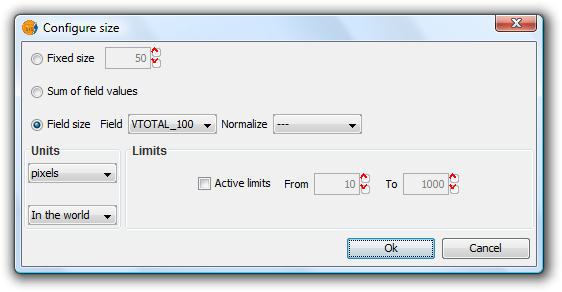
Bar Legend. Configuring size
There are three options for setting the size of the diagrams:
- Fixed Size: The largest bar will drawn to this size, and the rest will be drawn proportionately.
- Sum of field values: The size of the bars will be determined by the sum of all the records in the fields making up the chart.
- Field size: The size is obtained from the selected field and can be normalized if so desired. For example, a chart could be drawn to represent the number of votes for each political party by the size of the bar, while the overall size of the diagram could be determined by another field, such as number of habitants. In this example, the size of the graph would be larger for areas of greater population.
In addition to setting the size of the bars, the units can also be specified.
Units: Select units (meters, pixels ...) and representation (in the world or print layout), depending on your requirements. If the units are set to "in the world" then the size will depend on the View's zoom level, while selecting "print layout" results in a fixed size, both on the screen and when printed.
Active Limits: Limits can be specified if the size of the chosen field size is not set to the "Fixed Size" option.
Activating limits for the other options sets the minimum and maximum values of a particular measure (Sum of field values or Field size). Taking the limits into account, the intermediate field values are calculated in proportion to the values of the records of the field, or to the sum of the field values.
This option is used to restrict the drawing of bar charts to selected geometries.
The geometries can be selected either before or after configuring the bar chart size and display options.
In order to display bar charts for selected geometries, simply tick the check box “Draw only selection” in the pie legend configuration dialog.

Check to display bar charts for selected geometries only
The following image shows an example in which bar charts are only shown for selected geometries (shown in yellow).
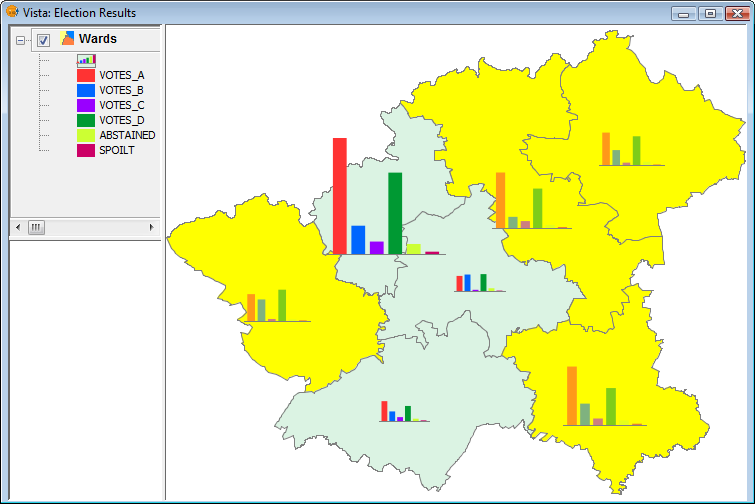
Example showing bar charts for selected geometries
Objects
Unique symbol
This is the default gvSIG legend type.
Represents all the elements of a layer using the same symbols. It is useful for when you need to show the location of a layer more than its any other attribute. The representation of its symbology depends on the type of geometry, this is further explained in the symbols section.
Saving and recovering legends
Save legend:
The legends that have been created can be saved so that you can use them on other occasions.
To save, click on the “Save legend” button.
A window will open with the save options: save legend with gvSIV (.gvl) format or standard exchange .sld format (currently supports SDL 1.0.0).
Legend recovery:
Legends that have been previously created can be recovered at any time. Click on the “Recover legend button” and select the legend you want to recover.









